WordPress user roles determine the level of access and permissions that different users have on a WordPress site. Each user role comes with specific capabilities, allowing users to perform certain actions on the site. Here's an overview of the standard WordPress user roles:
1. Administrator:
- Capabilities: Full control over the site, including managing other users, installing themes and plugins, and modifying site settings.
- Responsibilities: Site owner or manager with complete authority.
2. Editor:
- Capabilities: Can publish, edit, and delete any post or page, including those of other users.
- Responsibilities: Content manager with control over editorial aspects.
3. Author:
- Capabilities: Can publish, edit, and delete their own posts.
- Responsibilities: Content creator responsible for their posts.
4. Contributor:
- Capabilities: Can write and edit their own posts but can't publish them. Their posts require review and publication by an editor or administrator.
- Responsibilities: Content creator with limited publishing rights.
5. Subscriber:
- Capabilities: Can manage their profile and receive site updates.
- Responsibilities: Basic user with the ability to log in and consume content.
Managing User Roles:
-
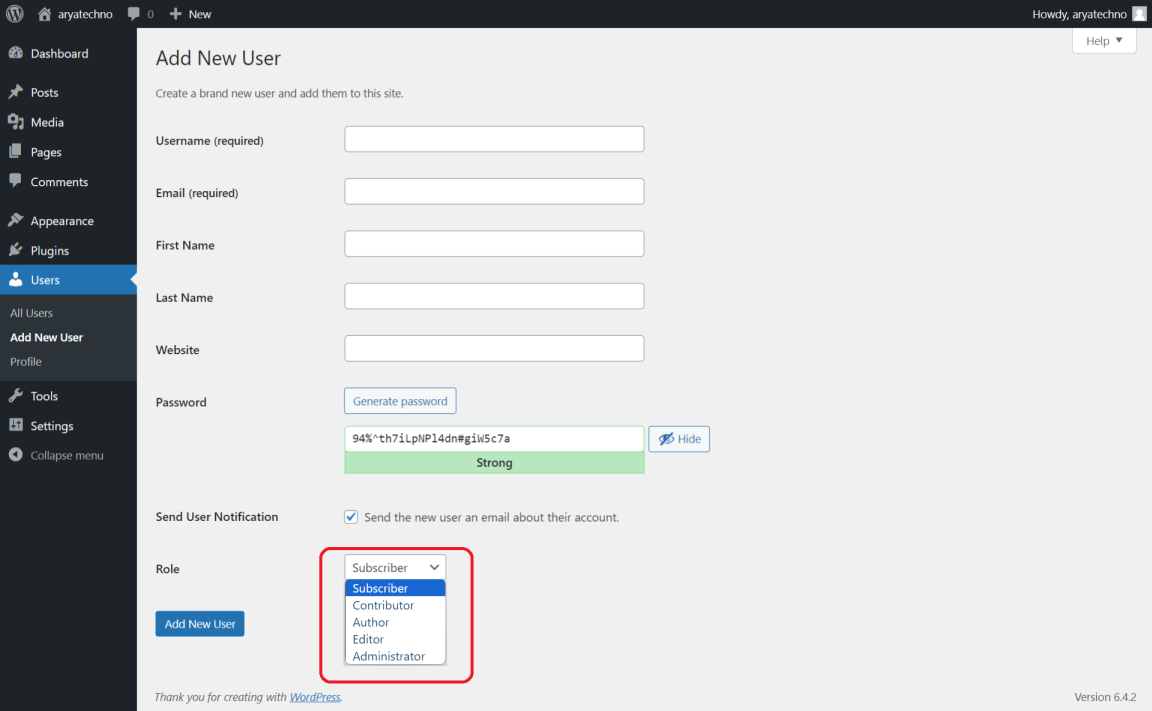
Adding a New User:
- Go to "Users" > "Add New."
- Fill in the required information, set the user role, and click "Add New User."
-
Editing Existing Users:
- Go to "Users" > "All Users."
- Hover over a user and click "Edit" to modify user details, including the user role.
-
Assigning User Roles During Invitation:
- When inviting a new user to your site, you can set their role while sending the invitation.
Custom User Roles:
In addition to the standard roles, some plugins allow you to create custom user roles with specific capabilities. However, managing custom user roles often requires a good understanding of WordPress development.

Comments